Python

Python
Code with a simple programming language that reads like kindergarten math, yet easily leads to lucrative jobs in research, software development, data science – Machine learning, Data Mining, big Data (Hadoop), statistics, Data visualization, data analytics.
>>>>>>>Maximize Success<<<<<<<
Python
What This Course Offers
This course is designed for the beginner, who do not have any experience at all with programming or development in order to learn how to program with Python. Topics include installing Python, data types and creating variables, input and output, decision making and repetition, iterators, list comprehension, functions, object oriented programming, inheritance, exception handling and using data structures.
Who Should Attend
- Project Managers
- Developers
- Analytics Professionals
- Anyone from any domain as no hard core programming knowledge is required
- Professionals who wish to switch to IT
- Those who had tried learning another programming language in the past and wish to restart with something simpler
- Wish to upgrade their skills
- wish to eventually steer their learning towards a related field
What You Get
- Course material
- Robust portfolio of programs to guide you at work
- Homework
- Assignments
- Projects
- Certificate of completion
- Portfolio reviews
- Resume support
- Mock interviews
- Career coaching
Duration
20 Hours (minimum)
Leaning Modes
- Classroom
- Online
- One on one private classes
Schedule
New session starts soon. Call 470-336-3966 or email contact@redbeartechnologies.com for details
Why Red Bear
Live Training
Qualified Instructors
Hands-On Training
Technical Assistance
Small Classes
Career Focused Training
Syllabus
Introduction
- What is Python
- Use cases
- Timeline
- Features
- Versions
- Distributions
Environment
- Installing Python for Mac
- Installing Python for Windows
- Setting path
- Documentation
- Help
- Command line shell, editors & IDEs
- Hello World
- Basic syntax
- Running Python script on Windows
- Running Python script on Unix
Getting Started
- Keywords
- Data Types
- Static vs Dynamic data types
- Fundamental Data Types
- Collection Types
- Mutable vs immutable objects
- Number Systems
- Variables
- Naming Conventions
- Print(), Type(), Id() functions
- Input() & raw_input functions
- Type Conversion functions
- Del keyword
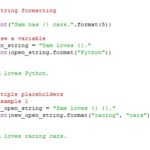
Strings
- Definition
- Single quote Strings
- String indexing
- String slicing
- String functions
- String methods
- String multiplication
- String concatenation
.
Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Short hand Assignment Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Membership Operators
- Identity Operators
- Precedence of Operators
- Evaluating expressions
Flow Control
- About Flow Control
- Elements of Flow Control
- Block/Clause
- Conditional Statements
- simple if
- if…else
- if…elif
- Looping Statements
- while loop
- while…else
- for loop
- using range() in for loop
- working with infinite loops
- nested loops
- Break statement
- Continue statement
- Pass statement
Collections
- Introduction
- List
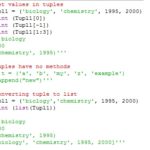
- Tuple
- Set
- Dict
- Indexing
- Slicing
- Functions for collections
- Methods for collections
- Iterating through a collection
- Operators for collections
- Keywords
- Nested collections
- Mathematical set operations
- Getting dictionary values
- Reading file data into a dictionary
- Counting with dictionaries
- Difference between list, tuple & set
- List, set & dictionary comprehensions
- Sorting
.
Functions
- Definition
- Calling a function
- Function parameters
- Argument types
- default
- non-default
- key word
- non key word
- arbitrary
- Return statement
- Return values
- Global & local variables
- Scope of global & local variables
- Call by value
- Call by reference
- Passing collections to functions
- Lambda functions/anonymous functions
- Passing functions to function
- Filter() & map() functions
Modules
- Definition
- Types
- Import statement
- Module Aliases/renaming a module
- From…import
- Reloading a module
- Built in properties
- Dir() function
- User defined modules
- Module search path
- Command line arguments
- Pre-defined standard modules
.
Packages
- Introduction
- _init_.py file
- Definition
- Importing from packages
- Defining sub packages
- Importing from sub packages
Exception Handling
- Definition
- Syntax errors
- Runtime errors
- Need for exception handling
- Predefined exceptions
- Predefined exception handling
- try, except, finally clauses
- Named except block
- Default except block
- Handling multiple exceptions
- Nested try, except, finally blocks
- User defined exceptions
- Raise, assert statements
File Handling
- Definition of file
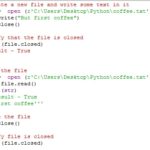
- Opening a file
- Reading data from a file
- Writing data to a file
- Closing a file
- Methods of file object
- Replacing the content of file
- Working with dictionaries
- Handling IO exceptions
Hear It From Our Students